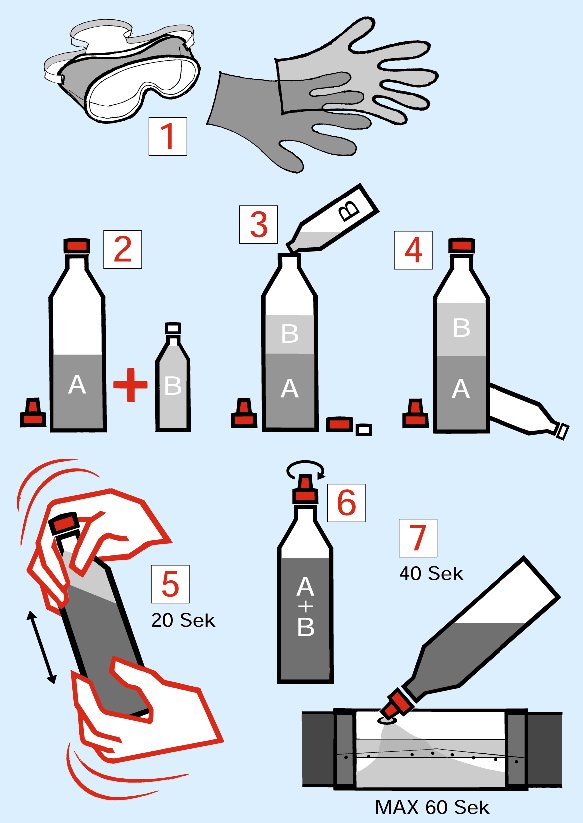
Urethanes
Urethanes are plastics produced from the reaction of an isocyanate and a polyol. Urethanes versatile chemistry offers possibilities for a wide variety of applications. Firm, light-foam urethane (10 kg/m3) is available.
Urethane’s main advantages are a low viscosity (typically 1 Pa·s), low curing temperature (50-70 °C), a very quick reaction time; if necessary (a few seconds), and low price. Urethane’s weaknesses are low strength properties and poor heat resistance; when compared to other thermoset plastics.
Urethane’s uses pertain to applications that include insulating foams, floats, core panels, coatings, adhesives, paints, engineering plastics, et al.. Urethanes used in the boating industry require regulatory approval.



