Reinforcements
Both continuous or discontinuous reinforcement fibers are used for either strengthening plastics or post-processing applications, e.g. carpets, fabrics, weaves, or braids. A matrix material, such as a thermosplastic, thermoset, ceramic, or metal, connects the yarns which are made from, for example, fiberglass, carbon fiber and aramid.
Reinforcements are used to improve the mechanical properties of plastics and their primary function is to withstand the different prospective loads acting upon the composite. The matrix material binds the fiber yarns together, protects them, and distributes loads. Even though the mechanical properties of plastics may be improved by filler or other agents added, actual strength properties are usually only accredited to the fibers which are manufactured and applied for this reason. We supply an extensive range of different reinforcements.
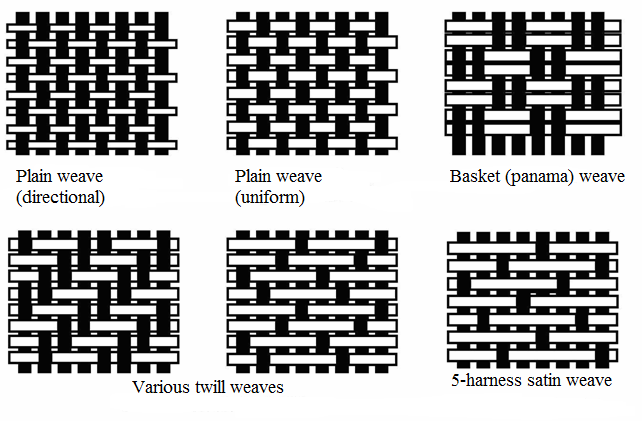
Shown below are several common types of fiber-constructed weaves. The fabric’s yarns functional properties can be either uniformly distributed or directional. In an evenly distributed weave, the warp and weft produce the same, or very close to the same, amount of reinforcement strength. In a directional weave, the majority of reinforcement strength, 95%, is isolated to either the weft or warp yarn-fibers. The general weave constructions are plain, twill, and satin.